Soft tissue injuries happen all the time. They are basically categorized as open wounds and closed wounds. Open wounds range from minor bruises and scrapes, to serious cuts, to even life threatening stab wounds to the abdomen.
While waiting for medical assistance to arrive, you can help the injured person by providing immediate general care for open wounds. Specific care depends on the type of soft tissue injury but general care for open wounds are basically the same and would include three things: controlling the bleeding, preventing infection, and using bandages and/or dressings.
Control the bleeding of open wounds

Open wounds can lead to severe bleeding and blood loss, if left uncontrolled; it can lead to serious problems or even death. You can help prevent severe blood loss by applying firm pressure over the wound using a clean or sterile dressing or pad.
If the wound is on a limb, elevate the injured area to reduce blood flow. Elevation sling or arm sling may be used if the arm is injured. For minor injuries, wound elevation and direct pressure are often enough to control bleeding. On the other hand, bleeding caused by major open wounds or cut blood vessels is often harder to contain. Applying pressure bandage may help, but usually, more advanced medical intervention such as stitching the severed blood vessel is necessary.
Prevent infection
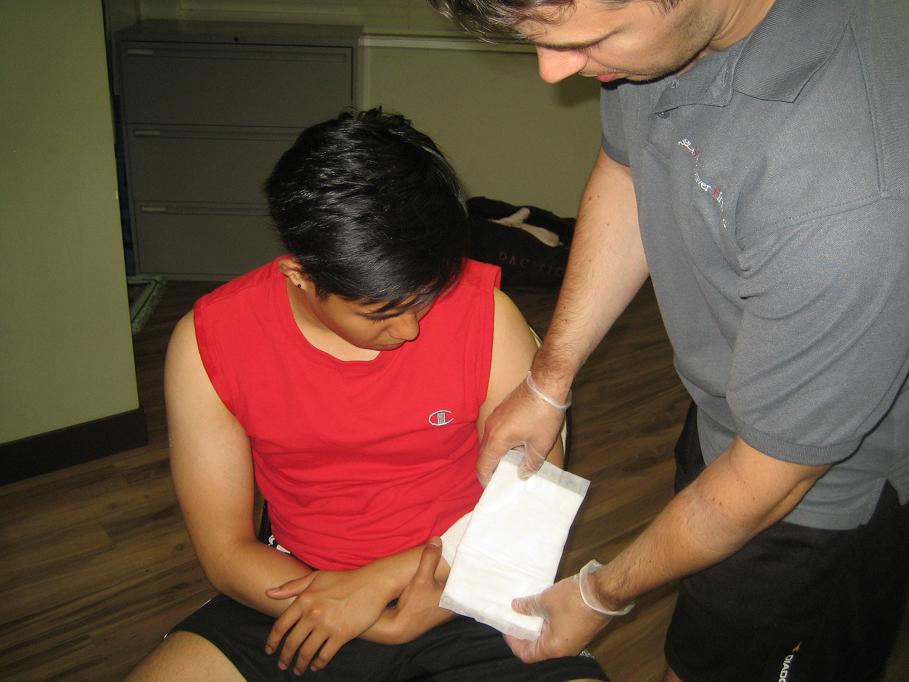
Open wounds are at increased risk for infection. You can minimize the chance of infection by using sterile dressings or pads. Dressings are applied directly onto the wound to absorb blood and other body fluids. It also protects the wound from infection.
In situations where emergency supplies are not available, do not waste your time searching for a suitable padding — you may use any clean cloth available. Be ready to use your hand or the patient’s hand to put the wound together.
It is not only the patient that must be protected from infection. First aiders should also ensure their own safety. As much as possible, avoid direct contact with the victim’s blood or other body fluids. Wear disposable gloves when providing first aid, if not available; place your hands inside a plastic bag instead.
In case there has been contact with blood or body fluids, wash your hands with soap and water as soon as possible.
Using Bandages/Dressings
Usually, dressings are porous that allow air to circulate and promote faster wound recovery. Standard dressings vary in size and thickness, with sizes ranging from 2 to 4 inches square. There are also specialized pads for use in specific types of wounds. There are large dressings that can be used for larger wounds or lacerations.
To keep dressings in place, you should also learn how to properly apply bandage. A bandage helps cover the injured part of the body. It also protects the wound from dirt and infection, as well as to provide support to the injured body part.
Sign up for a first aid class only with a reliable first aid course provider. Learn the basics of first aid and help save lives!
Related video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=klM8pk9OAik
FACT CHECK
https://www.healthline.com/health/open-wound